Adverb - Definition, Types, Use & Examples, Worksheet
Adverbs: The Versatile Words that Add Flair to Your Language
Table of content
1. Introduction
2. What Are Adverbs?
3. Types of Adverbs
4. Formation of Adverbs
5. Functions of Adverbs
6. Conclusion
7. Adverb Worksheet/ Exercise
8. FAQs
Definition :
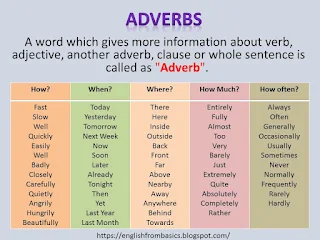
A word which gives more information about a verb, adjective, another adverb, clause or whole sentence is called as an "Adverb".
e.g. beautifully, now, away, very, generally, etc.1. Introduction
Adverbs are the versatile chameleons of language, capable of transforming our sentences with a touch of flair. These words are like magic dust, adding details, intensity, and clarity to our descriptions. Whether we're talking about actions, adjectives, or other adverbs, adverbs have got our back!
Here, we'll explore the world of adverbs, their functions, types, and how they can make your language sparkle.
2. What Are Adverbs?
Adverbs are like the seasoning of language – they enhance the flavors of our sentences. These special words modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more information about how, when, where, and to what extent something happened. Adverbs are the dynamic storytellers that help us paint vivid pictures with words.
It provides information like How? When? Where? How Much? How often? the action happens.
For example:- John drives the car slowly.
- John drives the car daily.
- John parks the car there.
- John drives the car very Fast.
- John drives the car always on Sundays.
Here you can see that the sentence is "John drives the car"
- When you ask How? The answer is slowly. "Slowly" is an adverb which is giving more information about the verb "drive".
Similarly, for When? daily, Where? there, How much fast? very & How often? always
- "Daily"- The adverb "Daily" gives more information about the verb "drive".
- "There" - The adverb "There" gives more information about the verb "park".
- "Very"- The adverb "Very" gives more information about the Adjective "Fast".
- "Always" - The Adverb "Always" gives more information about "on Sundays".
Most of the adverbs end with "ly" but it is not necessary.
For example: Continuously, Silently, Happily, Fast, Here, There, Sometimes, Often, etc.3. Types of Adverbs
Adverbs come in different forms, each with a specific purpose in our language. Let's explore the various types:1. Adverbs of Time:
These adverbs express when an action occurred. Examples include "now," "later," "soon," and "yesterday."2. Adverbs of Place:
These adverbs indicate where an action took place. Examples include "here," "there," "everywhere," and "somewhere."3. Adverbs of Manner:
These adverbs describe how an action was performed. Examples include "quickly," "carefully," "happily," and "efficiently."4. Adverbs of Degree:
These adverbs show the intensity or degree of an action. Examples include "very," "extremely," "quite," and "almost."5. Adverbs of Frequency:
These adverbs tell us how often an action occurs. Examples include "always," "often," "sometimes," and "rarely."4. Formation of Adverbs
Let's see how can we from adverbs from adjectives.1. Simply add "ly" to the adjective
For example: Kind-Kindly, Polite-politely, etc.2. When the adjective ends with "y", remove "y" and add "i" then add "ly"
For example: Happy- Happily, Angry- Angrily, etc.3. Other adverbs
For example: Simple-Simply, Whole-Wholly, Careful-Carefully, etc.5. Functions of Adverbs
Adverbs wear many hats in our sentences, and they serve various functions:1. Modifying Verbs:
- Adverbs modify verbs, telling us how an action was performed.
- She sings beautifully.
- He sings happily.
- I drive the car carefully.
2. Modifying Adjectives:
- Adverbs can also modify adjectives, providing more detail or intensity.
- He is extremely talented.
- He is very intelligent.
- We were extremely happy.
3. Modifying Other Adverbs:
- Adverbs can even modify other adverbs, emphasizing the degree of an action.
- She danced very gracefully.
- He answered very politely.
- The team played quite badly.
4. Modifying clause or sentence
- Adverbs can even modify clauses or entire sentences.
- Usually, We go for movies on weekends.
- Fortunately, John saved the puppy from falling into the river.
5. Expressing Time:
- Adverbs tell us when something happened or for how long.
- We will meet tomorrow.
- I was playing football yesterday.
6. Showing Place:
- Adverbs indicate where an action took place.
- They searched everywhere.
7. Demonstrating Manner:
- Adverbs describe how an action is performed.
- She spoke softly.
6. Conclusion
Adverbs are the versatile words that elevate our language, making it more expressive and engaging. They modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs, adding valuable details about time, place, manner, and degree.
Adverbs are like the spice that brings zest to our sentences, turning simple expressions into captivating narratives.
So, let adverbs be your creative allies, infusing your language with flair and excitement!
See Also : Preposition7. Adverb Worksheet/ Exercise
Instructions: Read each sentence carefully and identify the adverb.- She speaks softly to her baby.
- He quickly finished his homework.
- The car moved slowly through the traffic.
- They carefully planned their trip to Europe.
- The children played happily in the park.
- She danced gracefully across the stage.
- He eagerly volunteered to help with the project.
- The teacher spoke clearly to the students.
- They arrived late to the party.
- The rain fell steadily throughout the night.
- Adverb: softly
- Adverb: quickly
- Adverb: slowly
- Adverb: carefully
- Adverb: happily
- Adverb: gracefully
- Adverb: eagerly
- Adverb: clearly
- Adverb: late
- Adverb: steadily
FAQs: Adverb
1. What is an adverb?
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or other adverb, providing more information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens. Examples include "quickly," "very," "yesterday," and "here."2. What are the different types of adverbs?
There are several types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner, time, place, degree, frequency, and reason.3. What is an adverb of manner?
An adverb of manner describes how an action is performed. Examples include "slowly," "carefully," "happily," and "well."4. What is an adverb of time?
An adverb of time tells us when an action happens. Examples include "now," "soon," "yesterday," "later," and "always."5. What is an adverb of place?
An adverb of place indicates where an action occurs. Examples include "here," "there," "everywhere," "outside," and "nearby."6. What is an adverb of degree?
An adverb of degree explains the intensity or degree of an action, adjective, or another adverb. Examples include "very," "quite," "too," "almost," and "extremely."7. What is an adverb of frequency?
An adverb of frequency tells us how often an action occurs. Examples include "always," "never," "often," "sometimes," and "rarely."8. What is an adverb of reason?
An adverb of reason explains why an action happens. Examples include "therefore," "thus," "because," and "hence."9. Can adverbs modify adjectives and other adverbs?
Yes, adverbs can modify adjectives and other adverbs. For example, in "She is very tall," the adverb "very" modifies the adjective "tall." In "He runs incredibly quickly," the adverb "incredibly" modifies the adverb "quickly."10. How do you form adverbs from adjectives?
Many adverbs are formed by adding "-ly" to the end of an adjective. For example, "quick" becomes "quickly," and "happy" becomes "happily." However, some adverbs are irregular and do not follow this rule, such as "well" (from "good") and "fast" (same form as the adjective).References
- Azar B. S. & Hagen S. A. (2016). Understanding and using English grammar (5th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Quirk R., Greenbaum S., Leech G. & Svartvik J. (1985). A comprehensive grammar of the English language. Longman.
- Huddleston R. & Pullum G. K. (2002). The Cambridge grammar of the English language. Cambridge University Press.
- Swan M. (2016). Practical English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Carter R. & McCarthy M. (2006). Cambridge grammar of English: A comprehensive guide. Cambridge University Press.
- Parrott M. (2010). Grammar for English language teachers (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.