Future Perfect Continuous Tense - Structure, Uses & Examples
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Let's talk about the future perfect continuous tense! This tense helps us describe actions that will be ongoing for a period of time leading up to a specific point in the future. We rarely use this tense. Imagine you're thinking about what you'll have been doing before a certain event, like "I will have been studying for hours" or "She will have been working on her project all day."
Here's the easy part: To form the future perfect continuous tense, you use "will have been" followed by the base verb with "-ing" added to it. So instead of saying "I study," you say "I will have been studying."
Why does this matter? Well, lots of people search for help with grammar, English, or language learning. But sometimes, explanations can be hard to grasp. That's where we come in!
Understanding the future perfect continuous tense helps you talk about actions that will be ongoing up to a certain point in the future. It's like looking ahead and seeing what you'll have been up to by then. Plus, it's super handy for making plans or discussing future activities with detail.
So if you're learning English or just need a refresher, knowing the future perfect continuous tense is pretty cool. And guess what? It's not as tricky as it might seem!
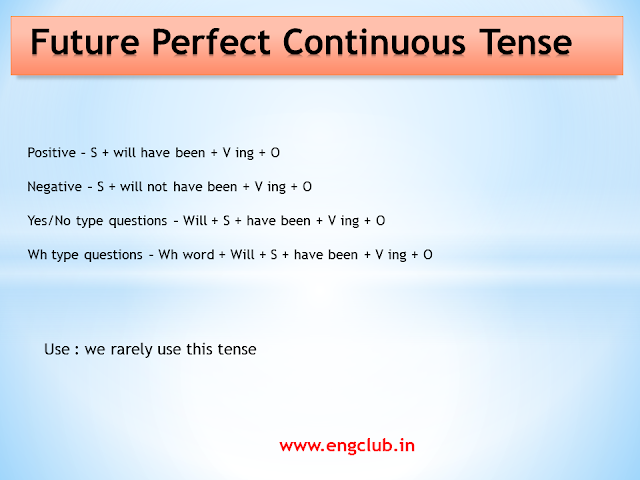
Structure of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Positive : S + will have been + V ing + O
- I will have been working on my project for five hours by noon.
- You will have been traveling around the world for a year by next summer.
- He will have been studying for the exam for three months by December.
- She will have been teaching at this school for ten years by the end of this year.
- It will have been raining for two hours by evening.
- We will have been waiting for the bus for thirty minutes by the time it arrives.
- They will have been playing soccer for two hours by noon.
- John will have been cooking dinner for an hour by 7 p.m.
- The students will have been preparing for the event for a week by tomorrow.
Negative: S + will not have been + V ing + O
- I will not have been working on my project for five hours by noon.
- You will not have been traveling around the world for a year by next summer.
- He will not have been studying for the exam for three months by December.
- She will not have been teaching at this school for ten years by the end of this year.
- It will not have been raining for two hours by evening.
- We will not have been waiting for the bus for thirty minutes by the time it arrives.
- They will not have been playing soccer for two hours by noon.
- John will not have been cooking dinner for an hour by 7 p.m.
- The students will not have been preparing for the event for a week by tomorrow.
Yes/No type questions: Will + S + have been + V ing + O + ?
- Will I have been working on my project for five hours by noon?
- Will you have been traveling around the world for a year by next summer?
- Will he have been studying for the exam for three months by December?
- Will she have been teaching at this school for ten years by the end of this year?
- Will it have been raining for two hours by evening?
- Will we have been waiting for the bus for thirty minutes by the time it arrives?
- Will they have been playing soccer for two hours by noon?
- Will John have been cooking dinner for an hour by 7 p.m.?
- Will the students have been preparing for the event for a week by tomorrow?
Wh type questions: Wh word + Will + S + have been + V ing + O + ?
- What will I have been doing for the past two hours by the time you arrive?
- Where will you have been living by next year?
- Why will he have been studying for six months before taking the exam?
- How long will she have been teaching at the school by the end of this year?
- How will it have been working for two hours without any issues?
- What will we have been waiting for by the time the bus arrives?
- Where will they have been playing soccer by noon tomorrow?
- How long will John have been cooking dinner by 7 p.m.?
- Why will the students have been preparing for the event for so long by next week?
Examples of Future Perfect Continuous Tense by uses
1. Actions That Will Have Been Ongoing Until a Future Time:
- By the time you arrive, I will have been waiting for two hours.
- She will have been studying English for five years by the time she graduates.
2. Duration of Actions Leading Up to a Future Point:
- By the end of the month, he will have been working on this project for six months.
- They will have been living in their new house for a year next month.
3. Emphasizing the Continuous Nature of Actions Before a Future Event:
- By the time the concert starts, they will have been rehearsing for weeks.
- I will have been practicing the piano for hours by the time you come over.
In the future perfect continuous tense, actions that will have been ongoing up to a specified time or event in the future are described. It's formed by using the future perfect tense of "have" (will have been) followed by "been" and the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Practice Time!
Let’s practice! Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in the Future Perfect Continuous Tense.- By the time she arrives, I _______ (wait) for two hours.
- They _______ (work) on this project all day by tomorrow.
- Will you _______ (study) for the exam for a week by then?
- She _______ (not practice) enough by the time of the performance.
- He _______ (already sleep) for hours when we call him.
- will have been waiting
- will have been working
- have been studying
- will not (won’t) have been practicing
- will have already been sleeping