Present Perfect Continuous Tense - Structure, Uses & Examples
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Let's chat about the present perfect continuous tense! It's a mouthful, but it's actually pretty straightforward. This tense is all about actions that started in the past, continue into the present, and might even keep going into the future. Imagine you're talking about something you've been doing recently, like "I have been studying" or "She has been working hard."
Here's the scoop: To form the present perfect continuous tense, you use "have been" or "has been" followed by the base verb with "-ing" added to it. So instead of saying "I study," you say "I have been studying."
Now, why is this helpful? Well, lots of people search for info on grammar, English, or even language learning. But sometimes, finding explanations that are easy to understand can be tough because there's a lot of complex stuff out there. That's where we come in!
Understanding the present perfect continuous tense helps you talk about actions or situations that have been happening over a period of time and are still ongoing. It's like saying, "Hey, I've been doing this thing for a while now!" Plus, it's great for emphasizing the duration of an activity.
So if you're learning English or just need a refresher, knowing how to use the present perfect continuous tense is pretty neat. And guess what? It's not as complicated as it sounds!
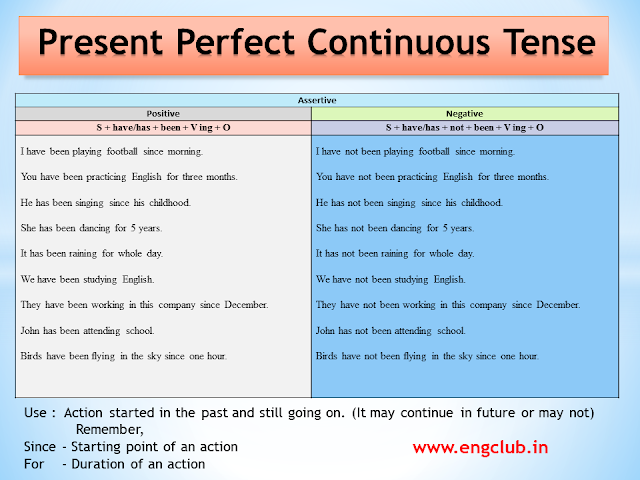
Verb Structure = have/has + been + Verb (ing)
For example- I have been waiting for doctor since 4 O'clock.
- I have been waiting for doctor for two hours.
- Since - Starting point of an action
- For - Duration of an action
Usage:
- We use the present perfect continuous tense to tell the action which started in the past and still going on. (It may continue in the future or may not)
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Structure
Positive : S + have/has + been + V ing + O
- I have been playing football since morning.
- You have been practicing English for three months.
- He has been singing since his childhood.
- She has been dancing for 5 years.
- It has been raining for the whole day.
- We have been studying English.
- They have been working in this company since December.
- John has been attending school.
- Birds have been flying in the sky for one hour.
Negative : S + have/has + not + been + V ing + O
- I have not been playing football since morning.
- You have not been practicing English for three months.
- He has not been singing since his childhood.
- She has not been dancing for 5 years.
- It has not been raining for the whole day.
- We have not been studying English.
- They have not been working in this company since December.
- John has not been attending school.
- Birds have not been flying in the sky for one hour.
Yes / No type question: Have/has + S + been + V ing + O + ?
- Have you been playing football since morning?
Wh type question: Wh word + have/has + S + been + V ing + O + ?
- Where have you been playing football since morning?
- How long has it been raining?
- Since when have you been playing football?
Examples of present perfect continuous tense by uses:
1. Actions Started in the Past, Still Ongoing:
- She has been studying for her exam all morning.
- They have been working on this project for weeks.
2. Continuous Actions Leading Up to the Present:
- He has been playing the guitar for hours.
- I have been waiting for you since 3 o'clock.
3. Emphasizing Duration of Action:
- We have been watching movies all evening.
- She has been practicing yoga for thirty minutes every day.
4. Recent Actions with Current Relevance:
- It's so muddy outside! It has been raining all day.
- I'm exhausted. I've been cleaning the house non-stop.
5. Actions with Result or Outcome:
- She's out of breath because she has been running.
- I'm really sore because I've been exercising a lot lately.
In the present perfect continuous tense, actions that started in the past and are still ongoing or just recently stopped are emphasized. It's formed by using the auxiliary verb "have" or "has" followed by "been" and the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Practice Time!
Let’s practice! Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.- I _______ (study) for the test for three hours.
- They _______ (wait) for the bus since 8 AM.
- She _______ (not feel) well lately.
- Have you _______ (work) on the project all day?
- He _______ (play) the piano for two years.
- have been studying
- have been waiting
- has not (hasn’t) been feeling
- been working
- has been playing
Keep practicing, and the Present Perfect Continuous Tense will become second nature. Happy learning!
FAQs: Present Perfect Continuous Tense
1. What is the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
It describes actions that started in the past and continue to the present or have recently stopped with present relevance.2. When do we use it?
For actions continuing up to now, recent actions with present results, and emphasizing duration.3. How do we form it?
Use have/has + been + base verb + ing.4. Common mistakes?
Using the wrong auxiliary verb and forgetting 'been'.5. Questions and negatives?
Use have/has for questions and have/has + not for negatives.References
- Murphy R. (2019). English grammar in use: A self-study reference and practice book for intermediate learners of English (5th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL). (n.d.). Verb tenses: Present perfect continuous tense explained.https://owl.purdue.edu
- BBC Learning English. (n.d.). Present perfect continuous tense: How and when to use it. https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish
- Quirk R., Greenbaum S., Leech G. & Svartvik J. (1985). A comprehensive grammar of the English language. Longman.
- Azar B. S. (2009). Understanding and using English grammar (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Swan M. (2005). Practical English usage (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Eastwood J. (1994). Oxford guide to English grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Thomson A. & Martinet A. V. (1986). A practical English grammar (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Celce-Murcia M. & Larsen-Freeman D. (1999). The grammar book: An ESL/EFL teacher's course (2nd ed.). Heinle & Heinle Publishers.
- Seely J. (2004). Oxford English grammar course: Basic. Oxford University Press.
- Nunan D. (2003). Practical English language teaching (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Richards J. C., & Schmidt R. (2010). Longman dictionary of language teaching and applied linguistics (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Lewis M. (1993). The English verb: An exploration of structure and meaning (2nd ed.). Collins ELT.
- Hewings M. (2005). Advanced grammar in use (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Biber D., Conrad S. & Leech, G. (2002). Longman grammar of spoken and written English. Pearson Education.
- Carter R. & McCarthy M. (2006). Cambridge grammar of English: A comprehensive guide to spoken and written grammar and usage. Cambridge University Press.