Present Perfect Tense - Structure, Uses & Examples
Present Perfect Tense
Let's dive into the present perfect tense! This one's all about connecting the past to the present. Imagine you're talking about experiences you've had, like "I have visited Paris" or "She has learned to play the piano."
Here's the scoop: With the present perfect tense, you're combining "have" or "has" with the past participle form of the verb. So instead of saying "I visit," you say "I have visited."
Now, why is this useful? Well, lots of folks search for info on grammar, English, or even language learning. But sometimes, finding easy-to-understand explanations can be tough because there's a lot of complex stuff out there. That's where we come in!
Understanding the present perfect tense helps you talk about experiences or actions that happened at some point in the past but still have relevance now. It's like saying, "Hey, I did this thing, and it's still important!" Plus, it's handy for talking about things you've done in your life so far.
So if you're learning English or just need a quick reminder, knowing how to use the present perfect tense is pretty awesome. And guess what? It's not as tricky as it might seem!
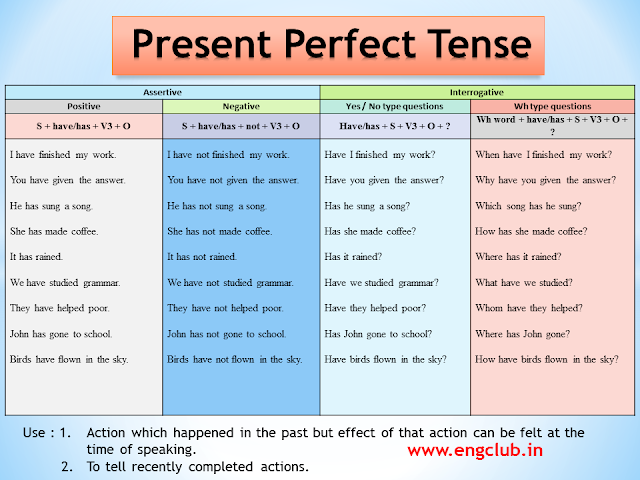
Verb Structure = have/has + Verb (III)
For example:- I have seen this movie before.
- You have started to practice English already.
- She has got a good job.
Usage
- To talk about an action which happened in the past, but the effect of that action can be felt at the time of speaking.
- I have already seen this movie
- You have started to practice English already.
- To talk about recently completed action.
- I have just finished my lunch.
- The train has just arrived.
- He has just entered the classroom.
Present Perfect Tense Structure
Positive : S + have/has + V3 + O
- I have finished my work.
- You have given the answer.
- He has sung a song.
- She has made coffee.
- It has rained.
- We have studied grammar.
- They have helped the poor.
- John has gone to school.
- Birds have flown in the sky.
Negative : S + have/has + not + V3 + O
- I have not finished my work.
- You have not given the answer.
- He has not sung a song.
- She has not made coffee.
- It has not rained.
- We have not studied grammar.
- They have not helped the poor.
- John has not gone to school.
- Birds have not flown in the sky.
Yes/No Type Questions: Have/has + S + V3 + O + ?
- Have I finished my work?
- Have you given the answer?
- Has he sung a song?
- Has she made coffee?
- Has it rained?
- Have we studied grammar?
- Have they helped the poor?
- Has John gone to school?
- Have birds flown in the sky?
Wh Type Question : Wh word + have/has + S + V3 + O + ?
- When have I finished my work?
- Why have you given the answer?
- Which song has he sung?
- How has she made coffee?
- Where has it rained?
- What have we studied?
- Whom have they helped?
- Where has John gone?
- How have birds flown in the sky?
Examples of Present perfect tense by uses :
1. Experiences in Life:
- I have visited Paris twice in my life.
- She has never ridden a horse before.
2. Actions Started in the Past, Still Relevant Now:
- They have lived in this neighborhood for ten years.
- He has worked at the company since 2010.
3. Recently Completed Actions:
- I have just finished my homework.
- We have already eaten dinner.
4. Unfinished Actions with 'For' or 'Since':
- She has been studying English for two years.
- He has been waiting for the bus since 3 o'clock.
5. Changes Over Time:
- The city has grown significantly since I moved here.
- Our relationship has become stronger over the years.
6. Multiple Actions at Different Times:
- I have read three books this month.
- They have traveled to several countries in the past year.
In the present perfect tense, actions or events that happened at an indefinite time in the past or have relevance to the present are expressed. It's formed by using the auxiliary verb "have" or "has" followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Practice Time!
- They _______ (visit) the museum.
- She _______ (not finish) her assignment yet.
- We _______ (live) here for three years.
- Have you ever _______ (try) sushi?
- He _______ (just arrive) home.
- have visited
- has not (hasn’t) finished
- have lived
- tried
- has just arrived
FAQs: Present Perfect Tense
1. What is the Present Perfect Tense?
2. When do we use it?
3. How do we form it?
4. Common mistakes?
5. Questions and negatives?
References
- Murphy R. (2019). English grammar in use: A self-study reference and practice book for intermediate learners of English (5th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL). (n.d.). Verb tenses: Present perfect tense rules and examples. https://owl.purdue.edu
- BBC Learning English. (n.d.). Present perfect tense: When and how to use it. https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish
- Dave’s ESL Cafe. (n.d.). Mastering the perfect tenses in English. https://www.eslcafe.com
- Quirk R., Greenbaum S., Leech G., & Svartvik J. (1985). A comprehensive grammar of the English language. Longman.
- Azar B. S. (2009). Understanding and using English grammar (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Swan M. (2005). Practical English usage (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Eastwood J. (1994). Oxford guide to English grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Thomson, A. & Martinet A. V. (1986). A practical English grammar (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Celce-Murcia M. & Larsen-Freeman D. (1999). The grammar book: An ESL/EFL teacher's course (2nd ed.). Heinle & Heinle Publishers.
- Seely J. (2004). Oxford English grammar course: Basic. Oxford University Press.
- Nunan D. (2003). Practical English language teaching (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Richards J. C. & Schmidt R. (2010). Longman dictionary of language teaching and applied linguistics (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Lewis M. (1993). The English verb: An exploration of structure and meaning (2nd ed.). Collins ELT.
- Hewings M. (2005). Advanced grammar in use (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Biber D., Conrad, S. & Leech G. (2002). Longman grammar of spoken and written English. Pearson Education.
- Carter R., & McCarthy M. (2006). Cambridge grammar of English: A comprehensive guide to spoken and written grammar and usage. Cambridge University Press.