Simple Present Tense - Structure, Uses, Examples & Rules to Add -s, -es, -ies
Simple Present Tense Made Easy: Structure, Rules, and Examples
As an English tutor helping students for several years, I created this beginner-friendly guide to the Simple Present Tense. Here you'll find rules, examples, and useful tips to help you speak fluently.
📘 Table of Contents
- 1. Verb 1st Form for Simple Present Tense
- 2. How to Add -s, -es, and -ies to Verbs: Rules & Examples
- 3. When and How to Use Simple Present Tense
- 4. Simple Present Tense Structure: Basic Sentence Patterns
- 5. Uses & Examples: Real-Life Sentences for Everyday Use
- 6. 100 Simple Sentences & Classroom Examples
- 7. Practice Time!
- 8. FAQs: Simple Present Tense
Let's talk about the simple present tense. It's a way we use verbs to talk about things that happen regularly, are true all the time, or are facts. Imagine you're telling someone about your daily routine, like "I eat breakfast every morning" or "She walks her dog every evening."
Here's the cool thing: It's super easy to use! You just need the base form of the verb, which means you don't add any extra endings like "-ed" or "-ing." For example, instead of saying "I walked," you say "I walk."
Now, why is this important? Well, lots of people search for info on grammar, English, or even language learning. But sometimes, finding simple explanations can be tough because there's a lot of complicated stuff out there. That's where we come in!
Understanding the simple present tense helps you speak and write correctly. Plus, it's crucial for building more advanced skills later on. So if you're learning English or just need a refresher, knowing how to use the simple present tense is a great place to start.
1. Verb 1st Form for Simple Present Tense
Verb Structure = Verb 1st form (Base form)
The verb 1st form in simple present tense is the base form of the verb (also known as V1), and it’s essential for forming correct English sentences, especially for beginners learning English grammar.
In the simple present tense, we use the base verb form with plural subjects like "I," "you," "we," and "they" (e.g., I eat, they play, we read).
For he, she, it, we usually add -s or -es (e.g., he plays, she watches). This rule helps in building daily use English sentences like “I walk to school” or “She drinks water.”
- I go to the office daily.
- He studies regularly.
Remember, If the subject is third person singular (He, She, It) or noun singular or singular indefinite pronoun, add "s" or "es" to the verb.
For example:- He, She, It – He plays Football every day.
- Noun Singular – John likes coffee.
- Singular Indefinite Pronoun – Everybody loves a holiday.
2. How to Add -s, -es, and -ies to Verbs in Simple Present Tense: Rules & Examples
1. Add "s" -
- Simply add "s" at the end of the verb. (Used for most of the verbs)
2. Add "es" -
- If the verb ends with ch, sh, x, o, ss, zz add "es".
3. Add "ies" -
- If the verb ends with "y" but before "y" there is a consonant, remove "y" and add "ies".
e.g. Fly - Flies, Cry - Cries, Try - Tries, etc.
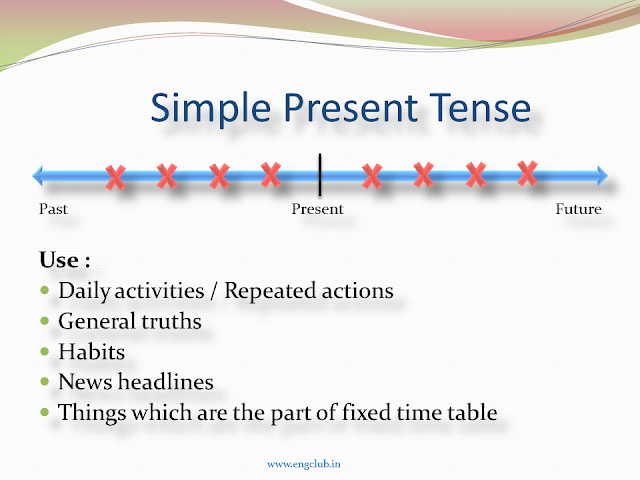
3. When and How to Use Simple Present Tense
- We use simple present tense to tell the actions which happen repeatedly.
- Jenny goes to school every day.
- She often writes poems.
- She drinks milk in the morning daily.
- To express general truths that exist and will exist in the future.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- Sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
- Plants absorb water from the soil.
- News headlines
Sometimes news headlines are written in simple present tense to keep the liveliness of the news
For example:- India wins the one-day cricket match against Australia.
- A car accident kills 5 people.
- To express future event, which is a part of a pre-decided timetable or we use this tense with future events.
- Exam starts at 10.00 am.
- The train departs at 06.00 pm.
- We will give it to her when she arrives.
4. Simple Present Tense Structure: Basic Sentence Patterns
4.1 Simple Present Positive Sentences: Structure and Examples with Verb Base Form
Positive : S + V1 + O
- I play football.
- You study daily.
- He goes to school.
- She makes tea.
- It rains in the rainy season.
- We speak English.
- They help the poor.
- John writes a story.
- Birds fly in the sky.
4.2 How to Form Negative Sentences in Simple Present Tense with Do/Does + Not
Negative : S + do/does + not + V1 +O
- I do not play football.
- You do not study daily.
- He does not go to school.
- She does not make tea.
- It does not rain in the rainy season.
- We do not speak English.
- They do not help the poor.
- John does not write a story.
- Birds do not fly in the sky.
4.3 Yes/No Questions in Simple Present Tense: How to Use Do and Does Correctly
Yes / No type questions : Do / Does + S + V1 + O + ?
- Do I play football?
- Do you study daily?
- Does he go to school?
- Does she make tea?
- Does it rain in the rainy season?
- Do we speak English?
- Do the help the poor?
- Does John write a story?
- Do birds fly in the sky?
4.4 WH Questions in Simple Present Tense: Structure and Common Examples
Wh type questions : Wh word + do/does + S + V1 + O + ?
- Where do I play football?
- What do you study daily?
- How does he go to school?
- When does she make tea?
- When does it rain?
- How do we speak English?
- How do they help the poor?
- What does John write?
- How do birds fly in the sky?
5. Simple Present Tense Uses & Examples: Real-Life Sentences for Everyday Use
1. Habits and Routines:
- Every morning, I wake up at 7 a.m.
- She always brushes her teeth before going to bed.
2. Facts and General Truths:
- The sun rises in the east.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
3. Scheduled Events:
- The train leaves at 9 a.m. tomorrow.
- Our class starts at 10 a.m. on Mondays.
4. Instructions and Procedures:
- First, you open the book. Then, you read the first chapter.
- We mix flour, eggs, and sugar to make a cake.
5. Hobbies and Interests:
- He plays guitar in a band.
- They collect stamps from different countries.
6. Feelings and Opinions:
- I love chocolate ice cream.
- She thinks learning new languages is fun.
6. 100 Simple Sentences & Classroom Examples
| Sr. No. | Sentence / Example |
|---|---|
| 1 | The teacher explains the lesson. |
| 2 | I write in my notebook. |
| 3 | We listen carefully. |
| 4 | He reads loudly. |
| 5 | She asks many questions. |
| 6 | You speak politely. |
| 7 | They sit in the front row. |
| 8 | The bell rings at 10 o’clock. |
| 9 | Students wear uniforms. |
| 10 | We study English every day. |
| 11 | I take notes during class. |
| 12 | My friend answers quickly. |
| 13 | We learn new words daily. |
| 14 | She teaches us grammar. |
| 15 | You learn from your mistakes. |
| 16 | They revise the topic regularly. |
| 17 | He checks our notebooks. |
| 18 | The class starts at 9 AM. |
| 19 | I ask questions when I don’t understand. |
| 20 | We follow classroom rules. |
| 21 | The teacher gives homework. |
| 22 | I do my homework every evening. |
| 23 | We play games after class. |
| 24 | The students answer politely. |
| 25 | You always come on time. |
| 26 | She brings her books every day. |
| 27 | I drink water from the bottle. |
| 28 | We learn something new every day. |
| 29 | They repeat after the teacher. |
| 30 | He uses simple words to teach. |
| 31 | The teacher writes on the board. |
| 32 | I understand the topic well. |
| 33 | We ask doubts in the class. |
| 34 | You help your classmates. |
| 35 | She reads the instructions. |
| 36 | They follow the rules. |
| 37 | My friend explains the answer. |
| 38 | The principal checks attendance. |
| 39 | I clean my desk daily. |
| 40 | We share our books. |
| 41 | She smiles during the lesson. |
| 42 | We open our textbooks to page ten. |
| 43 | The student answers the question. |
| 44 | I bring my lunch every day. |
| 45 | You check the homework before class. |
| 46 | The librarian helps us find books. |
| 47 | We enjoy our English class. |
| 48 | She listens to the teacher carefully. |
| 49 | I sit next to my best friend. |
| 50 | The monitor maintains silence. |
| 51 | We complete our classwork on time. |
| 52 | You read the story with interest. |
| 53 | He asks questions in every class. |
| 54 | The students form a line. |
| 55 | We respect our teachers. |
| 56 | I visit the library during break. |
| 57 | She uses colored pens to take notes. |
| 58 | They write neatly in their notebooks. |
| 59 | You answer the roll call. |
| 60 | The teacher calls out the names. |
| 61 | I underline important words. |
| 62 | We participate in classroom activities. |
| 63 | He uses the dictionary to find meanings. |
| 64 | She gives examples on the board. |
| 65 | You check your answers twice. |
| 66 | I follow the teacher’s instructions. |
| 67 | We enjoy doing projects together. |
| 68 | He carries his books in a backpack. |
| 69 | The student rings the bell. |
| 70 | We revise before tests. |
| 71 | You submit your assignments on time. |
| 72 | She sharpens her pencil. |
| 73 | I wait quietly for my turn. |
| 74 | We stand when the principal enters. |
| 75 | The teacher corrects our mistakes. |
| 76 | He closes the windows before leaving. |
| 77 | She opens her notebook quickly. |
| 78 | They clean the board after class. |
| 79 | You arrange the chairs properly. |
| 80 | The bell signals the end of the period. |
| 81 | I go to the washroom during break. |
| 82 | We draw pictures in art class. |
| 83 | She colors neatly within the lines. |
| 84 | You wear your ID card every day. |
| 85 | The students enjoy the story session. |
| 86 | I help the teacher distribute books. |
| 87 | We sing the national anthem. |
| 88 | The teacher checks our attendance. |
| 89 | You open the windows for fresh air. |
| 90 | I close the books after class. |
| 91 | We form groups for discussion. |
| 92 | She writes answers on the board. |
| 93 | The students clap after the performance. |
| 94 | You help carry the books. |
| 95 | I memorize new vocabulary. |
| 96 | We practice speaking in pairs. |
| 97 | He spells the words correctly. |
| 98 | She solves the math problems. |
| 99 | You underline the heading. |
| 100 | I enjoy learning English every day. |
See also: All 12 English Tenses With 100+ Sentences & Classroom Examples [Easy Guide]
7. Practice Time!
- She _______ (go) to school every day.
- They _______ (watch) TV in the evening.
- The cat _______ (chase) the mouse.
- I _______ (not like) broccoli.
- Does he _______ (play) tennis?
- goes
- watch
- chases
- do not (don’t) like
- play
English Tenses Comparison Table
| Tense | Usage | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Present Tense | Daily routines, facts | Subject + base verb / verb+s | She reads every day. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Actions happening now | Subject + is/am/are + verb+ing | I am studying English. |
| Present Perfect Tense | Recently completed actions | Subject + has/have + past participle | They have finished homework. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | From past to now | Subject + has/have been + verb+ing | He has been working since morning. |
| Simple Past Tense | Completed actions in the past | Subject + past verb | We visited the zoo yesterday. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Specific time past actions | Subject + was/were + verb+ing | She was cooking at 8 PM. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Before another past action | Subject + had + past participle | They had left before I arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Ongoing past action | Subject + had been + verb+ing | I had been reading for two hours. |
| Simple Future Tense | Future facts or decisions | Subject + will + base verb | She will call you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Action in progress in future | Subject + will be + verb+ing | I will be sleeping at 11 PM. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Done before a future time | Subject + will have + past participle | We will have arrived by noon. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Ongoing till future time | Subject + will have been + verb+ing | She will have been working for 5 years. |
📘 Learn All 12 English Tenses
8. FAQs : Simple Present Tense
1. What is the Simple Present Tense?
2. When do we use Simple Present Tense?
3. How do we form Simple Present Tense?
4. Simple Present Tense Common mistakes?
5. Simple Present Tense Questions and negatives?
References
- Murphy R. (2019). English grammar in use: A self-study reference and practice book for intermediate learners of English (5th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). Verb tense consistency. https://owl.purdue.edu
- BBC Learning English. (n.d.). Grammar lessons: Simple present tense. https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish
- Dave’s ESL Cafe. (n.d.). Grammar lessons for English learners. https://www.eslcafe.com
- Quirk R., Greenbaum S., Leech, G., & Svartvik J. (1985). A comprehensive grammar of the English language. Longman.
- Azar B. S. (2009). Understanding and using English grammar (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Swan M. (2005). Practical English usage (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Eastwood J. (1994). Oxford guide to English grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Thomson A. & Martinet A. V. (1986). A practical English grammar (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Celce-Murcia M. & Larsen-Freeman D. (1999). The grammar book: An ESL/EFL teacher's course (2nd ed.). Heinle & Heinle Publishers.
- Seely J. (2004). Oxford English grammar course: Basic. Oxford University Press.
- Nunan D. (2003). Practical English language teaching (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Richards J. C. & Schmidt R. (2010). Longman dictionary of language teaching and applied linguistics (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Lewis M. (1993). The English verb: An exploration of structure and meaning (2nd ed.). Collins ELT.
- Hewings M. (2005). Advanced grammar in use (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Biber D. Conrad S. & Leech G. (2002). Longman grammar of spoken and written English. Pearson Education.
- Carter R. & McCarthy M. (2006). Cambridge grammar of English: A comprehensive guide to spoken and written grammar and usage. Cambridge University Press.